Professor Ding Junjun’s Team from Zhongshan School of Medicine Drew Landscape of 3D Genome during Phase Transition
Source: Zhongshan School of Medicine
Edited by: Zheng Longfei, Wang Dongmei
Phase separation is widespread within cells, where thousands of proteins or nucleic acid molecules form a membrane-less "compartments" inside living cells, like oil droplets in water, and participate in multiple cellular processes without interfering with each other. 1,6-hexydiol (1,6-HD) is the only tool capable of dissolving phase-separated droplets simultaneously, so it has great potential to be applied to study the relationship between phase separation and other biological processes or structures at global-level. However, the conditions of 1,6-HD vary considerably between studies and may even trigger apoptosis, abnormal protein aggregation, chromatin "frozen" and other side effects, which greatly hinder the application of this tool. On the other hand, eukaryotic chromatin folds in the nucleus in a specific form, forming ordered three-dimensional structures in space, which are related to cell fate decision and disease occurrence. Recently, phase separation has been proposed to have a prominent role in 3D chromatin organization. However, there is only indirect or case evidence, and lack of global-level studies.
On 17 August 2021, the study of Professor Ding Junjun’s team entitled “Time-dependent effect of 1,6-hexanediol on biomolecular condensates and 3D chromatin organization” is published in
Genome Biology. For the first time, the using condition of 1,6-HD (1.5%, 2 min) with fewer side effects was optimized and tested on a variety of cell lines, and a time-resolved map of 3D chromatin structure upon1,6-HD treatment was provided to explore the relationship between phase separation and 3D chromatin organization.
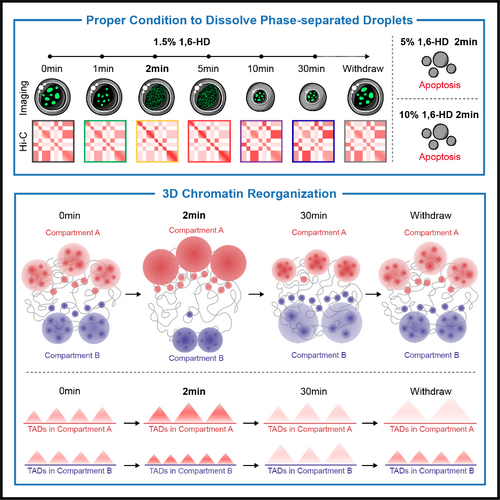
Time-dependent effect of 1,6-HD on phase-separated droplets and 3D chromatin organization
In this study, the researchers first analyzed the effects of different concentrations and treatment durations of 1,6-HD and found that short-term exposure to 1.5% 1,6-HD dissolved phase-separated droplets whereas long-term exposure caused aberrant aggregation without affecting cell viability. Based on this condition, the researchers drew a time-resolved map of 3D chromatin organization and found that short-term treatment with 1.5% 1,6-HD resulted in reduced long-range interactions, strengthened compartmentalization, homogenized A-A interactions, B-to-A compartment switch and TAD reorganization, whereas longer exposure had the opposite effects. Furthermore, the long-range interactions between phase-component-enriched regions were markedly weakened following 1,6-HD treatment.
In all, the study finds a proper 1,6-HD condition (1.5%, 2 min) to dissolve phase-separated droplets with limited side effects and provides a time-resolved map of chromatin organization during 1,6-HD treatment. The study demonstrate that 1,6-HD treatment has a time-dependent effects on phase-separated droplets and chromatin organization at different hierarchies. This time-resolved map would serve as a resource for exploring the role of phase separation in 3D chromatin organization.
The research was co-authored by Xinyi Liu, Ph. D Candidate and Shaoshuai Jiang, Postdoc, Zhongshan School of Medicine. Ding Junjun, Professor of Zhongshan School of Medicine at Sun Yat-sen University, is the sole corresponding author.
Link to the research article:
https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-021-02455-3
