Professor Jun Chen’s Team from Zhongshan School of Medicine and Professor Shoudeng Chen’s Team from the Fifth Affiliated Hospital jointly revealed the structure and new immunomodulating functions of SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a protein
Source: Zhongshan School of Medicine
Edited by: Tan Rongyu, Wang Dongmei
SARS-CoV-2 is highly contagious and causing the current global pandemic of COVID-19. As of March 14, 2021, a total of 119,212,530 confirmed cases and 2,642,612 deaths worldwide have been reported. According to previous reports, immune dysfunction is closely related to the progression of COVID-19. Severe patients will propagate a strong cytokine storm but often fails to produce a protective immune response, especially lacking effective virus-neutralizing antibodies. However, it is currently unclear about the specific molecular mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 factors regulating immune dysfunction.
Recently, Jun Chen’s Team from Zhongshan School of Medicine and Shoudeng Chen’s Team from the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University have analyzed the crystal structure and immunomodulating function of the SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a protein. It was found that ORF7a promoted the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines by CD14
+ monocytes, and at the same time, downregulated the expression of HLA-DR/DP/DQ molecules of CD14
+ monocytes, inhibited the antigen presentation ability of monocyte-derived macrophages, thereby facilitating the immune escape of SARS-CoV-2. In the process of SARS-CoV-2 infection, ORF7a protein may play a key role.
The collaborative team discovered for the first time that SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a could efficiently bind to CD14
+ monocyte-derived macrophages from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Simultaneously, using the single-crystal X-ray diffraction method, the 2.20 ? high-resolution crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a protein was reported for the first time. Through structural comparison analysis with the SARS-CoV ORF7a protein, it is found that the variant amino acid sites of SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a are concentrated in the larger β sheet, and the side chains are all facing outwards. SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a can activate human CD14
+ monocyte-derived macrophages to secrete abundant proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IL-1b, IL-8, and TNF-a. It is suggested that this is the potential functional interface of the viral protein.
More importantly, this study found that ORF7a can significantly downregulate the expression of HLA-DR/DP/DQ molecules in human CD14
+ monocyte-derived macrophages, indicating that SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a can inhibit the antigen presentation ability of monocyte-derived macrophages. This explains the clinical immune dilemma of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. That is, the patients present strong inflammatory responses, which should stimulated effective antiviral adaptive immune responses. However, due to the ORF7a protein, monocytes and macrophages cannot effectively present antigens, resulting in the lack of virus-specific neutralizing antibodies in the body, weakening the adaptive immune responses. Eventually, the inflammatory reaction becomes an ineffective cytokine storm, attacking the patient’s vital organs (such as lungs and brain), further aggravating the infection. This work brings important implications for further understanding the imbalance of immune function in severe patients with COVID-19 and the corresponding drug development.
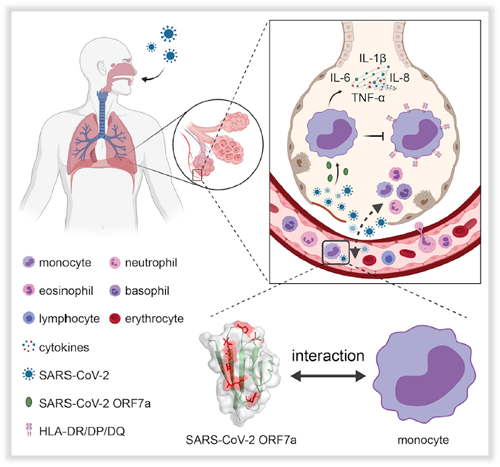
Fig. SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a protein regulates the imbalance of CD14
+ monocyte immune response in the progress of COVID-19.
The result of this study, “Structural insight reveals SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a as an immunomodulating factor for human CD14
+ monocytes”, was recently published in
iScience. The doctoral candidate Ziliang Zhou from the Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Chunliu Huang, a doctoral candidate from Zhongshan School of Medicine, and Zhechong Zhou, a doctoral candidate from the Fifth Affiliated Hospital are the co-first authors of the paper. Professor Jun Chen from Zhongshan School of Medicine and Professor Shoudeng Chen from the Fifth Affiliated Hospital are the paper’s co-corresponding authors.
Link to the paper:
https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(21)00155-3

