Prof. Hui Chao’s group at School of Chemistry made important achievements in the field of bioimaging agent
Source: School of Chemistry
Edited by: Tan Rongyu, Wang Dongmei
Compared with qualitative probes, quantitative probes are better suited to improve our understanding of biological processes and disease development. Owing to their advantageous synthetic versatility and photophysical properties, metal complexes have attracted a great deal of interest in this field. However, most of the reports so far have focused on single molecules. Their phosphorescence intensities are susceptible to environmental factors which may affect the accuracy of the results. Molecules with aggregation-induced emission properties may provide a solution to these problems. The accuracy of results can also benefit from the better photostability of aggregated states. Interestingly, despite their many advantages, this type of probe is currently extremely rare.
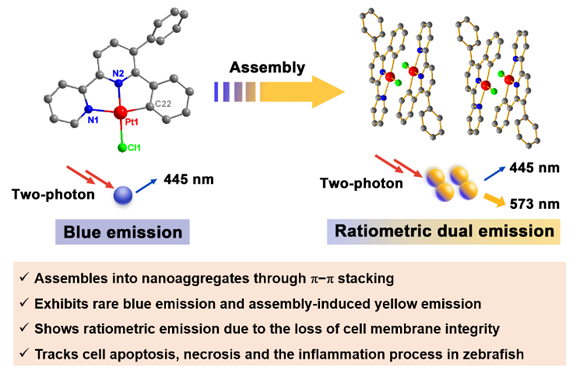
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the ratiometric dual emission applied in two-photon bioimaging.
Recently, a research team led by Professor Hui Chao of the School of Chemistry at Sun Yat-sen University constructed an organoplatinum(II) complex Pt1 with ratiometric dual emission for two-photon bioimaging. A phenyl group was added to the 6-phenyl-2,2'-bipyridine ligand to sterically block unwanted Pt-Pt interactions. Further theoretical calculation indicated that the forming Pt-Pt bond is antibonding, which is in turn disfavoured for Pt-Pt interaction and complementary the phenyl sterically blocks. Concentration-dependent ratiometric dual emission, including rare blue emission (
lem = 445 nm) and assembly-induced yellow emission (
lem = 573 nm), were observed under one- and two-photon excitation.
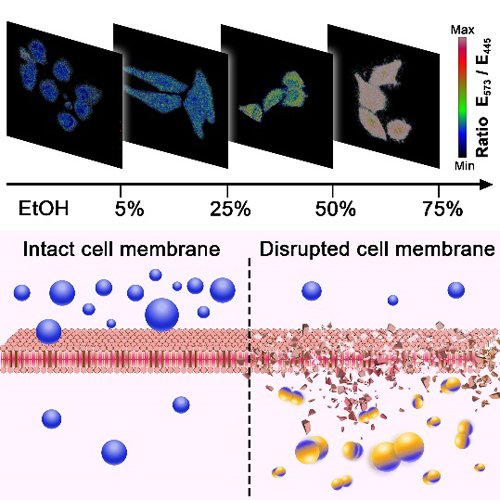
Figure 2. Pt1 is a quantitative indicator of the degree of cell membrane damage.
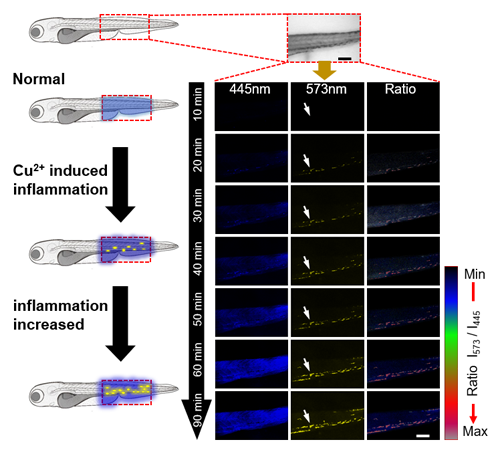
Figure 3. Real-time tracking of CuSO4 induced acute inflammation in zebrafish larvae.
It is well known that the cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. As the emission properties of Pt1 varied with the integrity of the cell membrane, its potential as a cell membrane integrity quantitative sensor was assessed. The research team verified that different concentrations of ethanol treatment can be used as a standard for cell membrane damage degree. Experimental results show that the blue emission intensity in all ethanol-treated cells remained unchanged while the yellow emission intensity was ethanol concentration-dependent, the ratio of yellow emission to blue emission can represent the damage degree of the cell membrane. The research team did more research and found out that Pt1 can be used not only to distinguish live cells, apoptosis, and necrosis but also to analyse the degree of cell membrane permeability during the process.
As acute inflammation is associated with the integrity of the plasma membrane, zebrafish larvae were exposed to CuSO4 (10 μM) followed by 5 μM of Pt1. As shown in Figure 3, located in the lateral line system of the larvae the complex forms yellow dots which gradually merge to form striations over time, indicating the presence of membrane damage. The ratio imaging results demonstrate that Pt1 can be applied to in situ real-time monitoring of the degree of membrane damage and to trace the inflammation process in vivo.
The research results have been published in
Angewandte Chemie International Edition (IF = 12.959) entitled "Supramolecular Assembly of An Organoplatinum(II) Complex with Ratiometric Dual Emission for Two-Photon Bioimaging". The first author is Dr. Cheng Ouyang, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-sen University. Associate Professor Yu Chen (Sun Yat-sen University), Dr. Xiting Zhang (University of Hong Kong), and Professor Hui Chao (Sun Yat-sen University) are the co-corresponding authors.
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21525105, 21778079, 21977126), the Ministry of Education of China (No. IRT-17R111), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 20lgjc01), and the Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou (No. 201806010136).
Link to the paper:
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202014043
