Source: Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital
Edited by: Tan Rongyu, Wang Dongmei
On June 11, 2021, the team of Prof. Tianxin Lin (Department of Urology, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital) published a research article entitled “A multicenter study to develop a non-invasive radiomic model to identify urinary infection stone in vivo using machine-learning” in
Kidney International, a renowned journal in the field of urology and nephrology. Prof. Lin and Prof. Xiaoguang Zou (the First People's Hospital of Kashi Prefecture) are co-corresponding authors of this article. Dr. Junjiong Zheng, Dr. Hao Yu from Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, and Dr. Jesur Batur from the First People's Hospital of Kashi Prefecture are co-first authors.
Urolithiasis, a condition of urinary stone formation in the bladder or urinary tract, is a common urological disease, which remains a major health problem worldwide with increasing incidence and prevalence. The high prevalence and recurrent of urolithiasis and its predominance in working age adults contributes to the substantial impact on the individual and society. Urinary stones can be classified into those caused by: infectious or non-infectious causes (infection stones and non-infection stones); genetic defects; or adverse drug effects (drug stones). Infection stones are complex aggregates of crystals amalgamated in an organic matrix that seem to be strictly associated with urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by urease-producing gram-negative organisms. They make up approximately 10–15% of urinary stone diseases. Due to the complex structure of infection stones and the high rates of recurrence, infection stone formers are one of the most challenging populations among urolithiasis patients. Infection stones were reported to have higher risk of postoperative infectious complications, which may potentially result in life-threatening conditions, such as severe sepsis and septic shock. In addition, the complete removal of the stones is crucial, since residual stones after surgery is an independent risk factor for infection stone recurrence. The therapeutic regimen of urolithiasis depends on the stone size, number, location, and composition. Among them, the stone composition is the basis for further diagnostic and management decisions. Knowledge of stone composition may aid in directing the appropriate choice of urological procedures and medical and lifestyle interventions to prevent stone recurrence. Whereupon, stone composition is usually unknown before treatment. Thus, in vivo determining urinary stone composition has become a recent research focus.
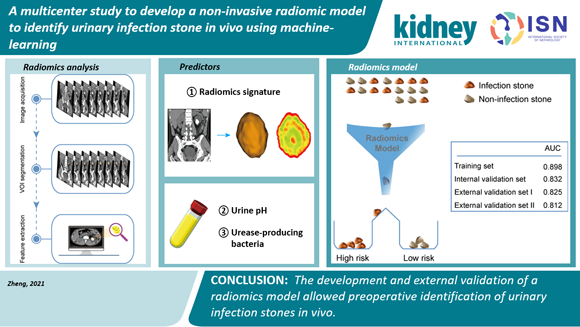
Radiomics is an approach that extracts high-throughput quantitative image features from radiographic medical images using data-characterization algorithms, which has the potential to uncover disease (lesion) characteristics that fail to be appreciated by the naked eye. Thus, radiomics method is reported to improve disease diagnosis, prognostic evaluation, and treatment response prediction, representing a promising approach to facilitating personalized and precise therapy.
In this study, a radiomics signature based on non-contrast CT images was developed for preoperatively identifying infection stones from non-infection stones. Moreover, by incorporating the radiomics signature, urease-producing bacteria in urine, and urine pH, a radiomics model was constructed. The radiomics model showed favorable discrimination and calibration with multicenter validation (AUC = 0.898 in the training set; AUC = 0.812-0.832 in the validation sets), providing a noninvasive tool for individualized preoperative assessment of the probability of having infection stones in patients with urolithiasis. This tool enables the analysis of the stone composition before removal, which may optimize disease management in urolithiasis and improve patient prognosis.
Link to the paper:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34129883/



