Source: Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital
Written by: Yamei Tang
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
On November 20th, 2018, an original research article entitled “Effect of Pregabalin on Radiotherapy-Related Neuropathic Pain in Patients With Head and Neck Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Trial”, conducted by Professor Yamei Tang from Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, was published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology (JCO, IF=26.3). After publication, Lancet Oncology commented on this article, pointing out that this study is the first randomized, controlled trial to investigate the effective of analgesic treatment for radiotherapy-related neuropathic pain among head and neck cancer patients, which offers high-quality evidence of treatment for radiotherapy-related neuropathic pain.
Head and neck cancers, especially nasopharyngeal carcinoma, have high incidence rate in southern China. Radiotherapy is the mainstay treatment for these patients. Head and neck cancer patients often suffer from pain and spasm in head and face after radiotherapy. It’s reported that chronic neuropathic pain occurs to about 31% of patients who underwent radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Neuropathic pain after radiotherapy seriously affects patients’ daily life and physical functions, and even leads to psychological disorders like anxiety and depression. In addition, conventional analgesics show poor effect on radiotherapy-related neuropathic pain. To date, there is no known treatment that has been proven to be effective in randomized clinical trials. So this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial of pregabalin versus placebo for neuropathic pain associated with radiotherapy can offer clinical implication to clinical practice.
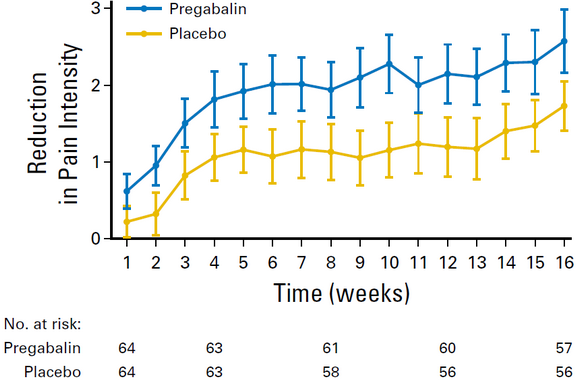
This clinical research investigated the efficacy and safety of pregabalin versus placebo in the treatment of radiotherapy-related neuropathic pain. The trial started in 2013 and lasted for 5 years. The participants were randomized to receive pregabalin or placebo with the principle of double blindness.The researchers evaluated the pain intensity, functional disorder caused by pain, emotional disorder and quality of life, and also recorded the side effects.The results demonstrated a significant analgesic benefit from pregabalinin patients with radiotherapy-related neuropathic pain. Moreover, patients treated with pregabalin hada significant decrease in functional interference and increased physical function, better emotional status, and improved quality of life compared with patients treated with placebo. This randomized controlled trial was the first time to confirm the analgesic effect of pregabalin on radiotherapy-related neuropathic pain with a mean pain reduction of 37%, and also had a beneficial effect on alleviating psychological distress and improving quality of life.
The trial offers clinical implications for the treatment of radiotherapy-related neuropathic pain, solves the problem in this field at a high level, and brings benefit to the patients with neuropathic pain.
Link to the article: http://ascopubs.org/doi/abs/10.1200/JCO.18.00896



